Understanding the Impact of Debt to Income Ratio with Student Loans on Your Financial Future
#### Debt to Income Ratio with Student LoansThe concept of debt to income ratio with student loans is becoming increasingly relevant for graduates entering……
#### Debt to Income Ratio with Student Loans
The concept of debt to income ratio with student loans is becoming increasingly relevant for graduates entering the workforce. This ratio is a crucial metric that lenders and financial institutions use to assess an individual's ability to manage monthly payments and repay debts. It is calculated by taking your total monthly debt payments and dividing them by your gross monthly income. For those with student loans, understanding how this ratio works can significantly influence your financial decisions, from applying for a mortgage to budgeting for everyday expenses.
#### Why is Debt to Income Ratio Important?
The debt to income ratio with student loans serves as a snapshot of your financial health. A lower ratio indicates that you have a manageable level of debt compared to your income, which can improve your chances of securing loans or credit. Conversely, a high ratio may signal to lenders that you are over-leveraged, making it more difficult to obtain financing for major purchases such as a home or car. In the context of student loans, this ratio can become particularly burdensome, especially for recent graduates who may be entering the job market with significant debt.
#### Calculating Your Debt to Income Ratio
To calculate your debt to income ratio with student loans, you first need to determine your total monthly debt payments. This includes your student loan payments, credit card payments, car loans, and any other monthly debt obligations. Next, find your gross monthly income, which is your income before taxes and other deductions. The formula is as follows:
\[
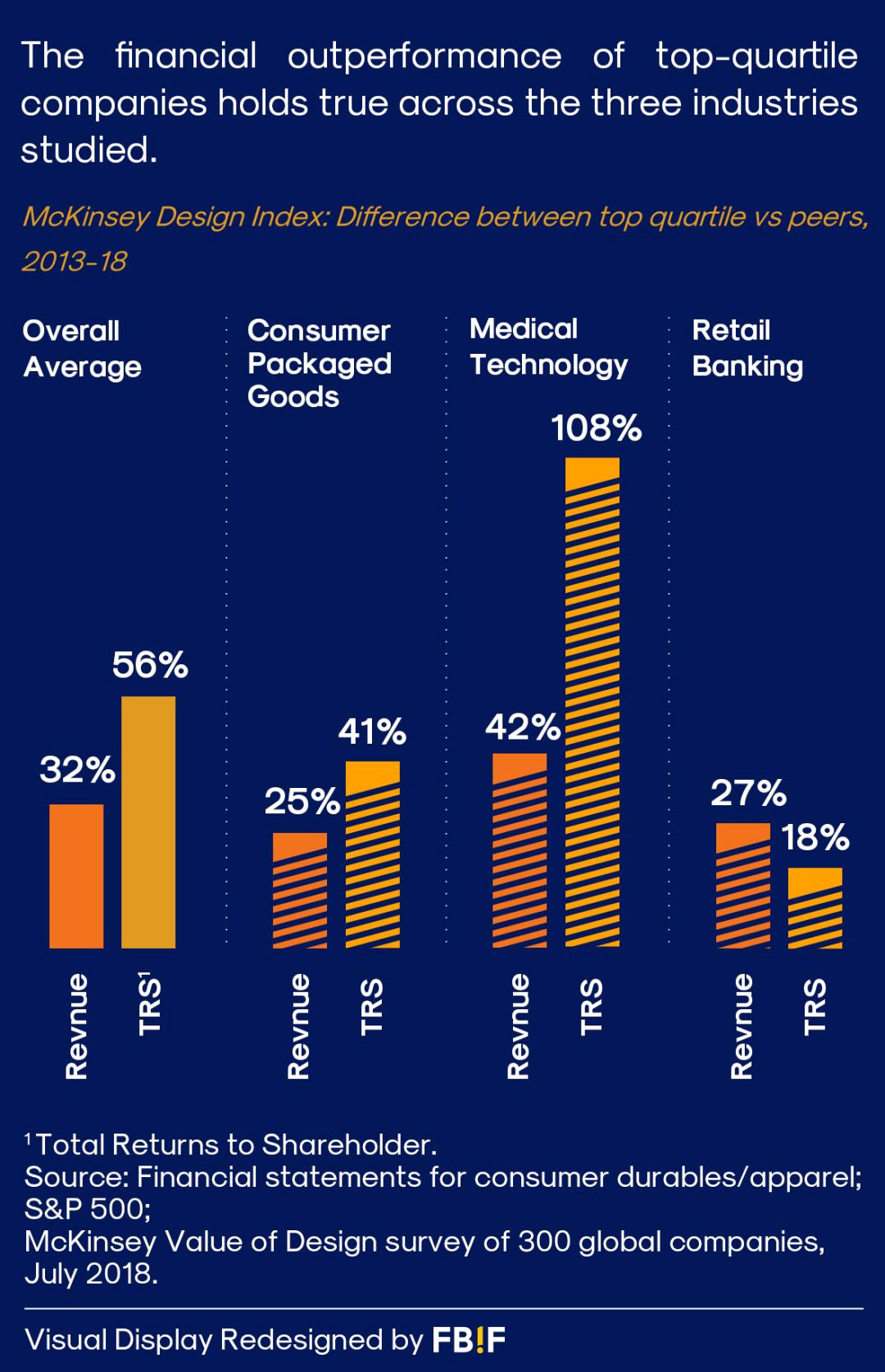
\text{Debt to Income Ratio} = \frac{\text{Total Monthly Debt Payments}}{\text{Gross Monthly Income}} \times 100
\]
For instance, if your total monthly debt payments amount to $1,200 and your gross monthly income is $4,000, your debt to income ratio would be:
\frac{1200}{4000} \times 100 = 30\%
#### What is a Good Debt to Income Ratio?
Generally, a debt to income ratio with student loans below 36% is considered healthy, with no more than 28% of that debt going toward housing expenses. However, individual circumstances can vary. Some lenders may allow higher ratios, especially if you have a strong credit history or additional income sources. It’s essential to be aware of your ratio and take steps to improve it if necessary.
#### Strategies to Manage Your Debt to Income Ratio
1. **Create a Budget**: Start by tracking your income and expenses. This will help you identify areas where you can cut back and allocate more funds toward your debt.
2. **Increase Your Income**: Look for opportunities to boost your income, whether through side jobs, freelance work, or asking for a raise at your current job.
3. **Pay Down Debt**: Focus on paying off high-interest debts first. This can lower your overall debt load and improve your debt to income ratio with student loans.

4. **Consider Income-Driven Repayment Plans**: If your student loans are overwhelming, explore options like income-driven repayment plans that can reduce your monthly payments based on your income.
5. **Limit New Debt**: Avoid taking on additional debt while you’re working to improve your ratio. This includes being cautious with credit cards and other loans.
#### Conclusion
Understanding your debt to income ratio with student loans is vital for making informed financial decisions. By calculating your ratio, recognizing its importance, and implementing strategies to manage it, you can pave the way for a more secure financial future. Remember, the goal is to maintain a healthy balance between your income and debt, allowing you to achieve your financial goals without being weighed down by overwhelming debt.